Updated Google Providers for StackQL Available
The latest versions of the Google-related providers for StackQL: google, googleadmin, googleworkspace, and firebase are available now. These updates include the latest services, resources and methods available from Google.
What's New
The latest release introduces several new services to the google provider, expanding your ability to manage and query Google Cloud resources:
- API Hub: Centrally manage and discover APIs across your organization
- Area Insights: Access location-based insights and analytics
- Cloud Location Finder: Identify optimal Google Cloud regions for your workloads
- Gemini Cloud Assist: Leverage Google's AI assistant for cloud operations
- Managed Kafka: Work with Google's fully-managed Apache Kafka service
- Observability: Enhanced monitoring and observability services
- Parallel Store: Interact with Google's high-performance storage solution
- Parameter Manager: Manage configuration parameters across services
- SaaS Service Management: Tools for managing SaaS offerings on Google Cloud
- Secure Source Manager: Google's secure, fully-managed source control service
- Security Posture: Assess and improve your cloud security posture
- Storage Batch Operations: Perform batch operations on Cloud Storage resources
Enhanced Documentation
We've also released enhanced user documentation to help you get the most out of these providers. Check out our comprehensive docs:
Getting Started
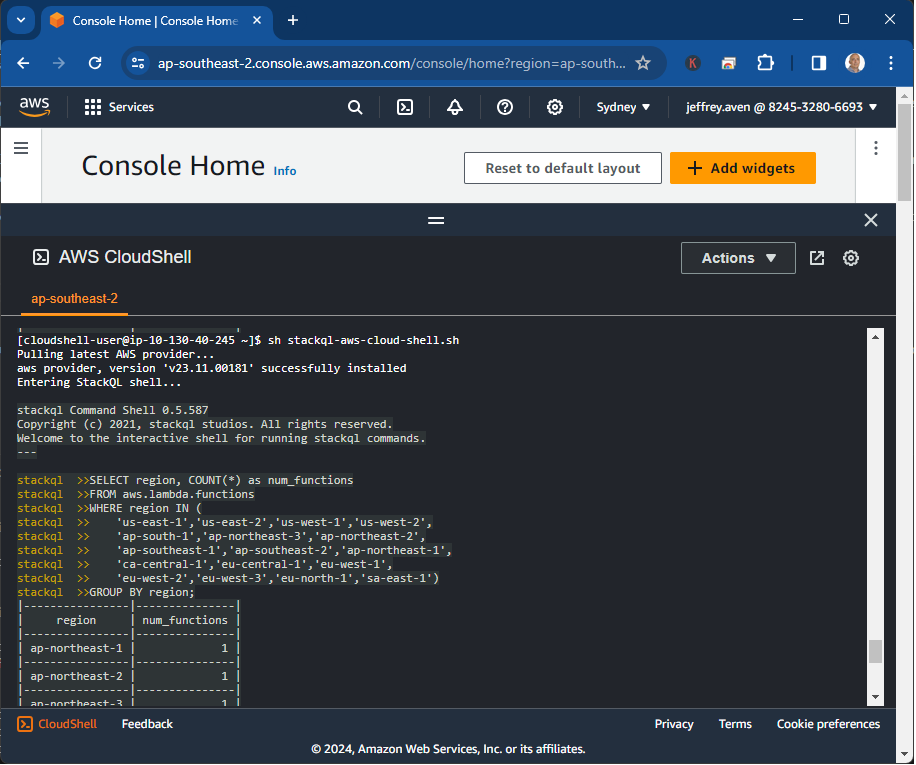
To start using these updated providers, simply pull the latest version from stackql shell or stackql registry command:
registry pull google;
registry pull googleadmin;
registry pull googleworkspace;
registry pull firebase;
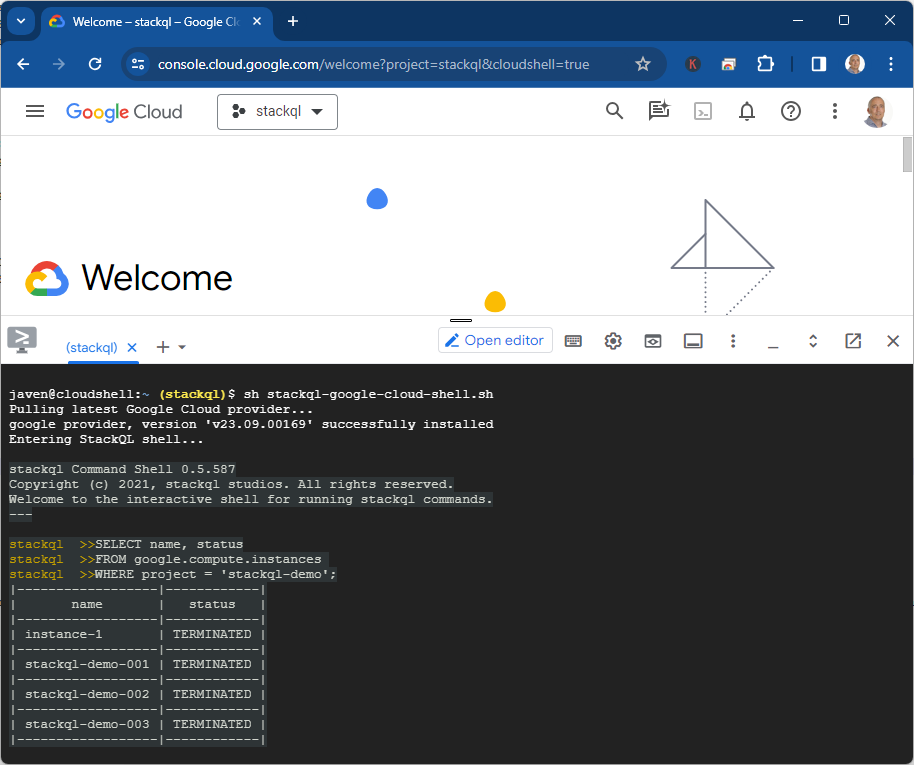
Then you can begin querying your Google resources with SQL:
SELECT name, region, status
FROM google.compute.instances
WHERE project = 'my-project';
Use Cases for the Google Provider
The Google provider for StackQL opens up numerous possibilities:
-
Infrastructure as Code: Manage your Google resources alongside other cloud providers in a unified IaC approach, see
stackql-deploy. -
Cost Optimization: Identify unused resources and opportunities for cost savings.
-
Security and Compliance: Audit account roles, permissions, and access patterns to ensure compliance with security policies.
-
Performance Monitoring: Track query performance, warehouse utilization, and identify optimization opportunities.
-
Cross-Provider Orchestration: Build workflows that span Google and other cloud providers, enabling sophisticated data and infrastructure pipelines.
-
Automated Reporting: Create automated reports on Google usage, performance, and costs.
⭐ us on GitHub and join our community!